©2019 Compass Learning Technologies ← Live Mathematics on the Web ← GeoGebra Assessment Showcase ← View My Data
View My Data
Learn How: Create Your Own Live GeoGebra Web Pages
OzDASL: Australian Data and Story Library
iNZight Lite: Data and Statistics for Everone
TI SensorTag: Real World Data in the Palm of your Hand
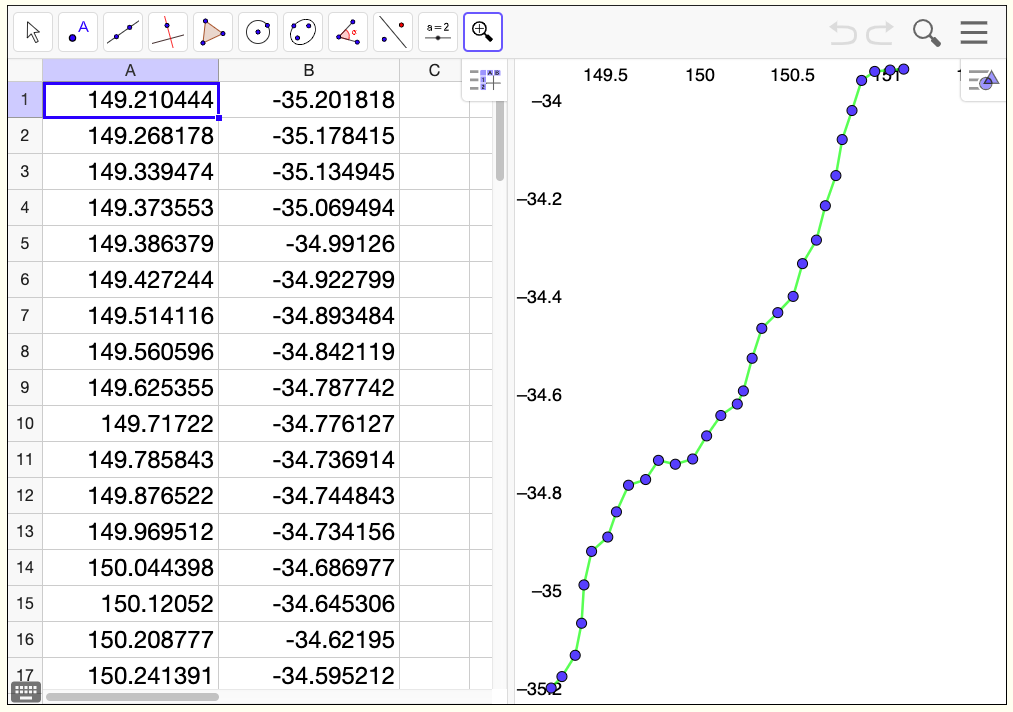
Quickly and easily view your datasets using this simple GeoGebra utility...
Tap the image to see how to use the web tools on this page... ⇓
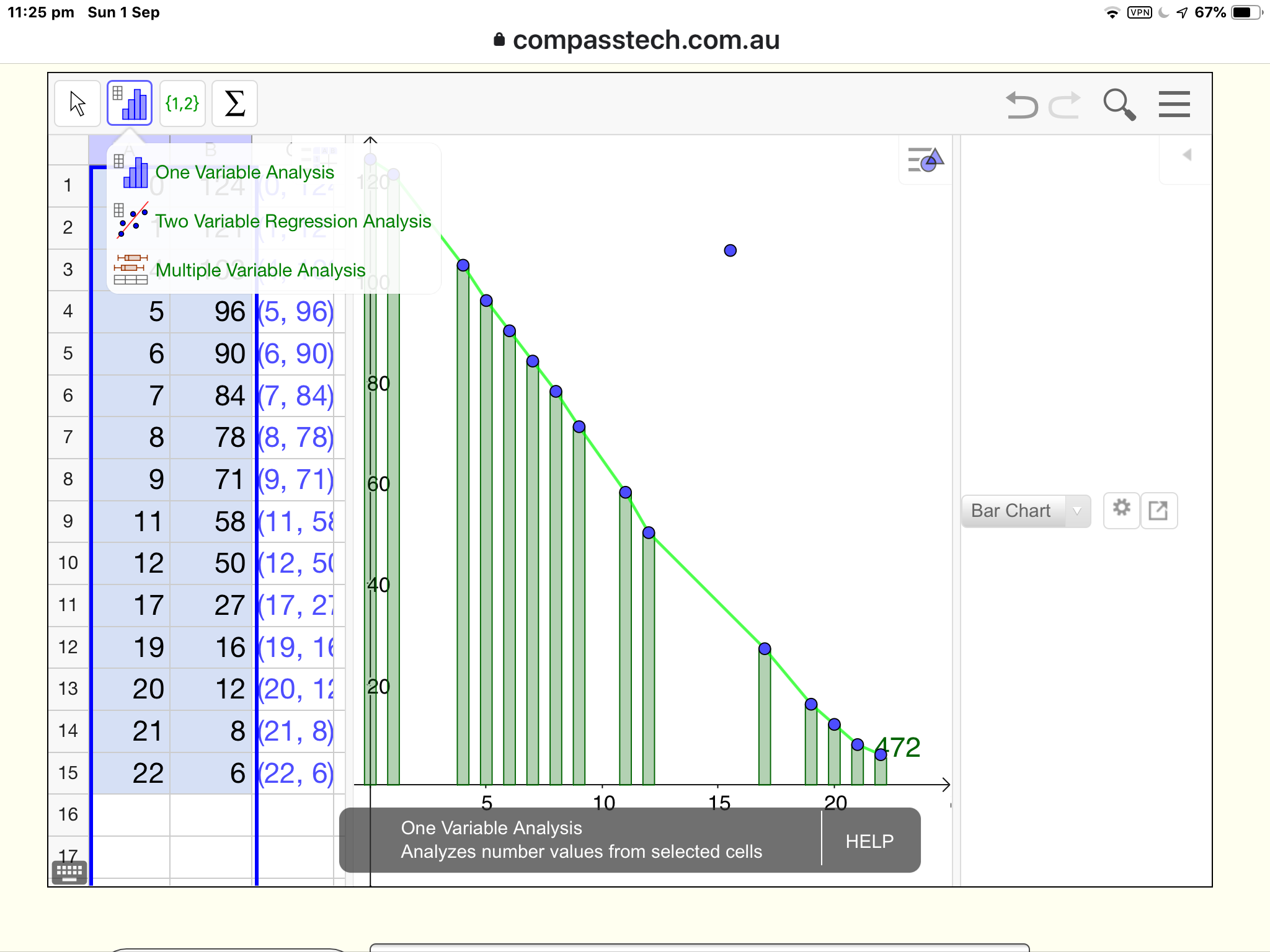
Tap the image to see how to use the GeoGebra Data Analysis tools ⇓
Enter one or two data sets into the fields below, and then select one of the Chart My Data buttons.
For individual (univariate) data sets (DataSet1 and/or DataSet2), each value will be numbered sequentially.
For paired (bivariate) data sets, DataSet1 becomes the horizontal (independent) value set and DataSet2 the vertical (dependent) set.
Note: To access GeoGebra's in-built Data Analysis tools, select list data from the spreadsheet (simplest way is to drag across the column headers to select those columns), and then select the Analysis menu as shown - it is the first of the three spreadsheet menus.
Explore the three menus available, and the various options available within these. They offer a couple of more options for you to view and analyse your data sets.