



(c) Find the equation, in Cartesian form, of the locus of the point z if
|
|
(e) Let P, Q and R represent the complex numbers w1, w2and w3 respectively. What geometric properties characterise triangle PQR if
|
|
Give reasons for your answer.
The diagram shows a complex plane with origin O. The points P and Q represent arbitrary non-zero complex numbers z and w respectively. Thus the length of PQ is |z - w |.
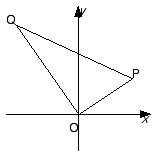 |
(i) Copy the diagram, and use it to show that
|
(ii) Construct the point R representing z + w. What can be said about the quadrilateral OPRQ?
(iii) If |z - w | = |z + w |, what can be said about the complex number 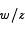 ?
?
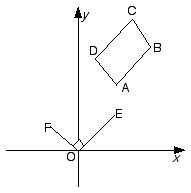 |
In the Argand diagram, ABCD is a square, and OE and OF are parallel and equal in length to AB and AD respectively. The vertices A and B correspond to the complex numbers w1 and w2 respectively.
(i) Explain why the point E corresponds to w2 - w1.
(ii) What complex number corresponds to the point F?
(iii) What complex number corresponds to the vertex D?
z1 and z2 are two complex numbers such that
|
(i) On an Argand diagram show vectors representing
|
(ii) Show that
|
(iii) If a is the angle between the vectors representing z1 and z2 show that
|
(iv) Show that
|
On an Argand diagram the point A represents the real number 1, 0 is the origin, and the point P represents the complex number z which satisfies the condition
|
(i) Show this information on a diagram and deduce that triangle OAP is isosceles.
(ii) deduce that the locus of P is the union of a circle and part of a straight line, and show this locus on your diagram.
(iii) Find z in mod-arg form if z also satisfies the condition
|
z1 and z2 are two complex numbers such that | z1 | = | z2 | and 0 < arg z1 < arg z2 < Pi/2. On an Argand diagram vectors OP and OQ represent z1 and z2 respectively. Angle QOP = Pi/3 and OPRQ is a parallelogram.
(i) Draw a diagram to show this information.
(ii) Find the value of
|
(iii) Show that
|
If
|
show that
|
Find the locus of z if
|
is (i) purely imaginary.
(ii) purely real.
If z is a point on the unit circle with arg z = a
(i) prove that
|
(ii) find the arguments of
|
in terms of a.
The four complex numbers 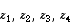 are represented on the complex (Argand) plane by the points A, B, C, D respectively.
are represented on the complex (Argand) plane by the points A, B, C, D respectively.
|
determine the possible shape(s) for the quadrilateral ABCD.
E is the centre of a square ABCD lettered anticlockwise on the Argand diagram. E and A are the points -2 + i and 1 + 5i respectively.
Find the complex numbers represented by the points B, C and D.
All care but no responsibility taken with these solutions. Comments, corrections and suggestions would all be most welcome: send to Stephen Arnold.
Back to Review of Complex Numbers